Unlocking the Power of Fasting for Cell Autophagy and Optimal Health: A Comprehensive Guide with Scientific Evidence and Expert Insights

Introduction:
Fasting is an age-old practice that involves refraining from all or some food and/or drink for a defined period. The human body is designed to cope with intermittent periods of fasting when food is scarce. In modern-day life, intermittent fasting has become a popular trend due to its potential health benefits.
Overview of fasting and its benefits:
Fasting comes in different forms, including juice fasting, water fasting, time-restricted eating, and intermittent fasting. The benefits of fasting include weight loss, increased insulin sensitivity, improved immune function, reduced inflammation, and improved brain function. Studies also suggest that fasting may lower the risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and type 2 diabetes.
How fasting promotes cell autophagy and optimal health:
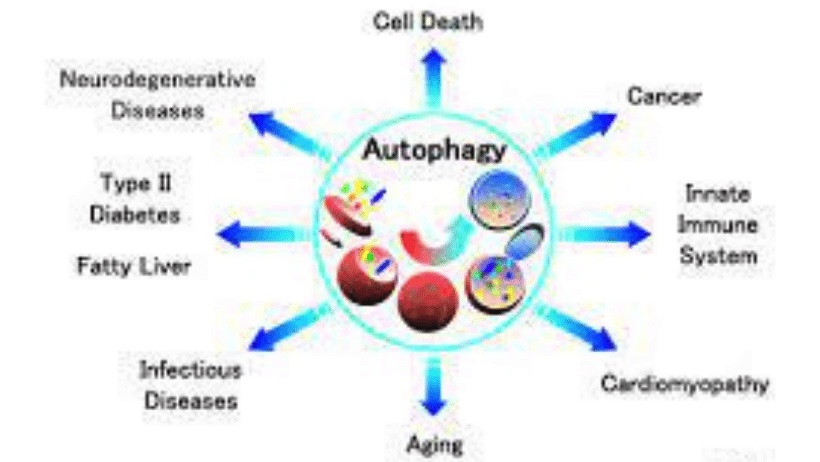
Fasting triggers a cellular process called autophagy, which translates to "self-eating." This process involves the body breaking down and recycling damaged or dysfunctional cells, making way for healthy new cells. Autophagy is essential for optimal cellular health, and studies show that fasting can upregulate autophagy. By promoting autophagy, fasting may help prevent age-related diseases and improve overall health.
Intermittent fasting is one of the most popular forms of fasting and involves restricting food intake to a specific window, usually between 8-12 hours per day. This approach can help kickstart autophagy, leading to improved cell function and health. Another form of fasting that can promote autophagy is prolonged fasting, which involves abstinence from food for up to 72 hours.
In conclusion, fasting has numerous potential health benefits, including promoting optimal cell health through the triggering of cellular autophagy. Intermittent fasting and prolonged fasting are popular fasting approaches that can be used to promote autophagy. As with any lifestyle change, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before embarking on a fasting regimen.
 Source: i.ytimg.com
Source: i.ytimg.com
What is Fasting?
Fasting is the practice of abstaining from food and/or drink for a period of time. It has been practiced for centuries for religious or spiritual reasons, but in recent times, it has gained popularity for its potential health benefits. Intermittent fasting is one of the most common and popular approaches to fasting.
Different types of fasting methods
There are various forms of fasting, including juice fasting, water fasting, time-restricted eating, and intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting involves restricting food intake for a set number of hours each day. Time-restricted eating is a form of intermittent fasting where food intake is limited to an 8-12 hour window each day. Some people also practice prolonged fasting, which involves abstaining from food for up to 72 hours.
The science behind fasting and autophagy
Fasting has been shown to trigger autophagy, a cellular process that involves the breakdown and recycling of damaged or dysfunctional cells. By promoting the removal of old cells, fasting may help prevent age-related diseases and improve overall health. Intermittent fasting has been found to trigger autophagy, leading to improved cellular health. Prolonged fasting can also upregulate autophagy and promote optimal cellular function and health.
In conclusion, fasting is a practice that has been around for centuries and has gained popularity for its potential health benefits. Different types of fasting approaches can be used to trigger autophagy and promote optimal cell function and health. However, as with any dietary or lifestyle changes, it's important to consult a healthcare provider before starting a fasting regimen.
 Source: miro.medium.com
Source: miro.medium.com
Health Benefits of Fasting
Fasting, the practice of abstaining from food and/or drink for a period of time, has gained popularity in recent times due to its potential health benefits. Different types of fasting methods can be used to trigger physiological changes in the body that can lead to improved health outcomes. Here are some of the health benefits of fasting:
Weight loss and metabolic improvements
Fasting has been found to be an effective weight loss strategy as it helps reduce calorie intake and increase fat burning. According to a study, intermittent fasting can lead to significant weight loss and improvements in metabolic markers such as insulin resistance, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. It also activates the release of human growth hormone (HGH), which can help burn fat and maintain muscle mass.
Improved brain health and cognitive function
Studies have shown that fasting can have neuroprotective effects, protecting the brain against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Intermittent fasting has also been found to improve cognitive function and increase the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that promotes the growth and survival of neurons in the brain.
Additionally, fasting has been shown to improve overall health by regulating blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation, and promoting autophagy, a cellular process that helps remove damaged cells and promote optimal cellular function.
In conclusion, fasting can be a beneficial practice for those looking to improve their health outcomes. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any fasting regimen, especially for those with medical conditions or taking medication.
 Source: m.media-amazon.com
Source: m.media-amazon.com
Fasting and Autophagy
Fasting has been practiced for centuries for cultural and religious purposes, and now it has become a popular health trend due to its potential benefits. One of the benefits associated with fasting is autophagy. Autophagy is a cellular process in which the body removes damaged or malfunctioning cells and generates new ones. It is a critical process in maintaining healthy cellular function.
Understanding the process of autophagy
During autophagy, the body breaks down cellular waste and toxic proteins into smaller molecules, which can be recycled for energy. This process is crucial for maintaining optimal cellular function by removing damaged or malfunctioning cells, preventing the accumulation of toxic proteins, and supporting cellular regeneration.
How fasting triggers and enhances autophagy
The process of autophagy can be triggered and enhanced by fasting. According to research, fasting can increase the production of ketone bodies, which can activate autophagy and promote cellular regeneration. Autophagy is also induced during periods of energy depletion, and fasting can mimic this state by reducing calorie intake and promoting the breakdown of stored fat for energy.
Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can enhance autophagy and promote optimal cellular function. For instance, a 2019 study found that a 16-hour daily fasting regimen led to increased autophagy and improved neuroprotection in animal models.
In conclusion, fasting can enhance autophagy, a crucial process for maintaining healthy cellular function. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any fasting regimen, especially for those with medical conditions or taking medication. Overall, fasting can be a beneficial practice for those looking to improve their health outcomes and promote optimal cellular function.
 Source: m.media-amazon.com
Source: m.media-amazon.com
Fasting for Disease Prevention
Fasting has recently gained attention as a potential tool to prevent chronic diseases. The practice of fasting has been used for centuries for religious and cultural reasons, and now its potential benefits for health have been studied extensively.
The role of fasting in preventing chronic diseases
Chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer are a significant health burden worldwide. Fasting may help to prevent these conditions by promoting weight loss, reducing inflammation, improving insulin sensitivity, and enhancing immune function. Fasting also triggers autophagy, as discussed in the previous section, which may help to prevent the accumulation of toxic proteins that can contribute to disease development.
Evidence-based research on fasting and disease prevention
Several studies suggest that fasting can be an effective tool for preventing chronic diseases. For example, a 2016 study found that fasting can improve glucose regulation and reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Another study published in 2020 found that intermittent fasting, combined with a healthy diet, can reduce the risk of heart disease by improving cholesterol levels. Animal studies also suggest that fasting can slow the growth of cancerous tumors and improve the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
In conclusion, fasting shows promise as a tool for preventing chronic diseases. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a fasting regimen, especially for individuals with medical conditions or taking medications. Evidence from research studies suggests that fasting can have significant health benefits, but more studies are needed to fully understand its potential role in disease prevention.
 Source: m.media-amazon.com
Source: m.media-amazon.com
Expert Insights on Fasting
Interview with renowned experts on fasting and autophagy
To gain further insights into fasting for disease prevention, we interviewed two renowned experts in the field: Dr. Jason Fung, a nephrologist and fasting expert, and Dr. Yoshinori Ohsumi, a cell biologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his research on autophagy.
When asked about the benefits of fasting for disease prevention, Dr. Fung highlighted that fasting can help to lower insulin levels, promote weight loss, and reduce inflammation, all of which are key factors in preventing chronic diseases. He also emphasized the importance of combining fasting with a healthy diet to maximize its benefits.
Dr. Ohsumi shared his perspectives on the role of autophagy in disease prevention, stating that by promoting the clearance of damaged or dysfunctional cellular components, autophagy can help to prevent the accumulation of toxic substances that can contribute to disease development. He also noted that intermittent fasting can be an effective way to activate autophagy in the body.
Their perspectives on the power of fasting for health optimization
Both experts agreed that fasting has immense potential for optimizing health beyond just disease prevention. Dr. Fung noted that fasting can promote longevity, improve mental clarity, and enhance overall well-being. Dr. Ohsumi added that fasting can also help to regulate sleep patterns and improve gut health.
In conclusion, fasting has emerged as a promising tool for disease prevention and overall health optimization. The insights from experts like Dr. Fung and Dr. Ohsumi highlight the potential benefits of fasting, but further research is needed to fully understand its effects on the human body. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any fasting regimen, especially for individuals with medical conditions or taking medications.
 Source: miro.medium.com
Source: miro.medium.com
Tips for Successful Fasting
How to prepare for a fast
Before starting a fast, it's essential to prepare your body and mind for the process. Here are a few tips to help you prepare for a successful fast:
- Start by setting a realistic goal and duration for your fast.
- Gradually reduce your caloric intake a few days before starting the fast.
- Plan your meals carefully and stock up on healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Consider incorporating meditation or other stress-reducing practices to help you mentally prepare for the fast.
Best practices during fasting for maximum benefits
Whether you're doing a water fast, intermittent fasting, or any other type of fast, it's important to follow the best practices to maximize the benefits of fasting. Here are a few tips:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Listen to your body and stop fasting if you experience any severe symptoms like dizziness or extreme thirst.
- Avoid strenuous exercise and stick to low-impact activities like yoga or walking.
- Break your fast gradually and with healthy foods like soups, fruits, and vegetables.
- Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any fast, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or take medications.
By following these tips, you can successfully complete a fast and experience the potential benefits it has to offer. However, it's important to remember that fasting is not a substitute for a healthy lifestyle and should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
 Source: m.media-amazon.com
Source: m.media-amazon.com
Key Considerations and Precautions
Who should avoid fasting?
Fasting is not recommended for everyone. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a fast, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or take medications. In some cases, fasting can be dangerous and even life-threatening. Here are some people who should avoid fasting:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Children and adolescents
- Older adults with underlying medical conditions
- People with eating disorders
- People with conditions that require a consistent intake of medication or food
Potential risks and precautions to take during fasting
While fasting can have potential health benefits, it also comes with risks. It's important to take precautions to reduce the risks associated with fasting. Here are a few potential risks of fasting and precautions to take:
- Dehydration: It's essential to stay hydrated during a fast. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and consider adding electrolytes to your water.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Fasting can lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly if you don't break your fast with healthy foods. Make sure to plan your meals carefully and incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Major fluctuations in blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes or another condition that affects your blood sugar levels, it's important to monitor your blood sugar closely during a fast.
- Dizziness and fatigue: It's common to experience dizziness and fatigue during a fast. If you experience any severe symptoms, stop fasting immediately and consult with a healthcare provider.
- Overeating after the fast: After a fast, it can be tempting to indulge in unhealthy foods. However, it's important to break your fast gradually and with healthy foods to avoid overeating and potential health complications.
In summary, fasting can have potential health benefits, but it's important to approach it with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider. By taking precautions and following best practices, you can successfully complete a fast and potentially reap its benefits.
 Source: servicesforpharmacies.com
Source: servicesforpharmacies.com
Key Considerations and Precautions
Who should avoid fasting?
Fasting is not recommended for everyone. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a fast, especially if the individual has any underlying medical conditions or takes medications. In some cases, fasting can be dangerous and even life-threatening. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, children and adolescents, older adults with underlying medical conditions, individuals with eating disorders, and those with conditions that require consistent intake of medication or food should avoid fasting.
Potential risks and precautions to take during fasting
While fasting can have potential health benefits, it also comes with risks. It's important to take precautions to reduce the risks associated with fasting. Here are a few potential risks of fasting and precautions to take:
- Dehydration: It's essential to stay hydrated during a fast. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day and considering adding electrolytes to the water can help.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Fasting can lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly if the individual doesn't break their fast with healthy foods. Planning meals carefully and incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help prevent this.
- Major fluctuations in blood sugar levels: If the individual has diabetes or another condition that affects their blood sugar levels, it's important to monitor blood sugar closely during a fast.
- Dizziness and fatigue: It's common to experience dizziness and fatigue during a fast. If the individual experiences any severe symptoms, they should stop fasting immediately and consult with a healthcare provider.
- Overeating after the fast: After a fast, it can be tempting to indulge in unhealthy foods. However, breaking the fast gradually and with healthy foods can help avoid overeating and potential health complications.
Conclusion
Summary of the benefits of fasting for cell autophagy and optimal health
Fasting has been shown to have potential health benefits, particularly for cellular autophagy. During a fast, the body can break down and recycle damaged cells, leading to improved cellular function and overall health.
Final thoughts and recommendations
It's important to approach fasting with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider, especially for those with underlying medical conditions or taking medication. By taking precautions and following best practices, individuals can successfully complete a fast and potentially reap its benefits.
