Fasting vs. Dieting: Which is More Effective in Lowering Cholesterol?
Introduction
 Source: pub.mdpi-res.com
Source: pub.mdpi-res.com
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that plays a crucial role in our body's functioning. However, when levels of cholesterol become elevated, it can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease and stroke. In an effort to combat high cholesterol, many individuals turn to different methods such as fasting and dieting. Fasting involves periods of restricted food intake, while dieting focuses on making specific changes to one's eating habits. Both of these approaches have been studied for their potential effects on lowering cholesterol levels. This article seeks to explore the effectiveness of fasting and dieting as cholesterol-lowering methods, delving into the science behind these practices and comparing their pros and cons. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each approach, individuals can make informed decisions about which method may be most effective for them in managing their cholesterol levels.
Definition of cholesterol and its impact on health
 Source: i.dietdoctor.com
Source: i.dietdoctor.com
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in the cells of the body. While it is essential for normal body functioning, high levels of cholesterol can have detrimental effects on health. Cholesterol is carried through the bloodstream by lipoproteins, specifically low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, can build up in the walls of arteries and lead to cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. On the other hand, HDL cholesterol, known as "good" cholesterol, helps remove excess LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. Maintaining healthy levels of cholesterol is crucial for overall well-being and preventing these chronic conditions. According to the American Heart Association, high blood cholesterol affects around 95 million Americans. Therefore, finding effective methods to lower cholesterol levels is of paramount importance.
Explanation of fasting and dieting as cholesterol-lowering methods
 Source: fshn.illinois.edu
Source: fshn.illinois.edu
Fasting and dieting are two methods commonly used to lower cholesterol levels. Fasting involves abstaining from food for a specific period of time, while dieting focuses on making dietary changes to promote better health. Both approaches aim to reduce cholesterol levels and improve overall cardiovascular health. Fasting can lead to weight loss, which in turn can lower cholesterol levels. Intermittent fasting has gained popularity as it allows for periods of eating and fasting, providing potential benefits for cholesterol management. Dieting involves following specific meal plans that are low in saturated fat and cholesterol, which can help regulate cholesterol levels. Adopting a heart-healthy diet recommended by organizations like the American Heart Association can lead to significant improvements in cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health.
Understanding Fasting
 Source: images.indianexpress.com
Source: images.indianexpress.com
Fasting is the practice of voluntarily abstaining from food or certain types of food for a specified period of time. There are different types of fasting, including intermittent fasting and water fasting. Intermittent fasting involves alternating between periods of eating and fasting, while water fasting involves consuming only water for a designated period. Both types of fasting have been shown to have various benefits, such as weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation. Additionally, research suggests that fasting can also have a positive impact on cholesterol levels, leading to lower levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before attempting any fasting regimen to ensure it is done safely and effectively.
Different types of fasting and their benefits
 Source: www.stylecraze.com
Source: www.stylecraze.com
There are several different types of fasting that individuals can follow to help lower their cholesterol levels. One popular method is intermittent fasting, which involves alternating periods of eating and fasting. This approach has been shown to improve cholesterol profiles by reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Another type of fasting is water fasting, in which individuals only consume water for a designated period. This can also lead to improvements in cholesterol levels, as well as helping to lower blood pressure. Overall, fasting can be an effective method for reducing cholesterol and improving cardiovascular health.
Effects of fasting on cholesterol levels
 Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Fasting has been shown to have positive effects on cholesterol levels. When you fast, especially for an extended period of time, your body goes into a state of ketosis where it starts burning stored fat for energy. This process can lead to a reduction in LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and an increase in HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Fasting can also help improve triglyceride levels, which are another type of fat found in the blood. Research studies have shown that intermittent fasting, in particular, can be effective in reducing both total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels. However, it is important to note that the effects of fasting on cholesterol may vary depending on factors such as overall diet and individual health conditions.
Exploring Dieting
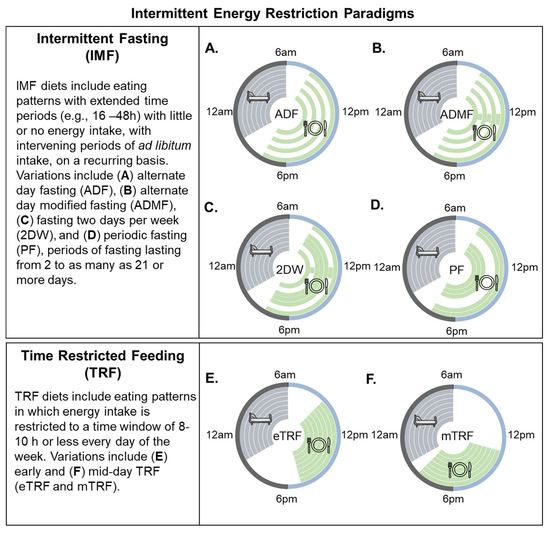 Source: www.mdpi.com
Source: www.mdpi.com
Dieting is a widely practiced method for lowering cholesterol levels. There are various types of diets that have been proven effective in reducing cholesterol. One popular diet is the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This diet has been shown to lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Another effective diet for lowering cholesterol is the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which focuses on reducing sodium intake and increasing consumption of fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products. The American Heart Association also recommends a low-cholesterol diet that limits saturated fats and trans fats. Dieting can have numerous benefits on cholesterol reduction and overall health when combined with regular exercise and lifestyle modifications.
Types of diets for lowering cholesterol
 Source: i0.wp.com
Source: i0.wp.com
There are several types of diets that have been shown to be effective in lowering cholesterol levels. One common diet is the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats such as olive oil. This diet also includes moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy products. Another popular diet for reducing cholesterol is the Portfolio diet, which focuses on incorporating foods that are rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, barley, and legumes. Additionally, the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet has been found to not only lower blood pressure but also reduce cholesterol levels. This diet promotes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products while limiting sodium intake. Finally, the vegetarian and vegan diets eliminate animal products and are often associated with lower cholesterol levels due to their plant-based nature. Overall, these different diets offer various approaches to managing cholesterol levels and can be tailored to individual preferences and dietary restrictions.
Benefits of dieting on cholesterol reduction
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in reducing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health. By making dietary changes, individuals can effectively lower their cholesterol levels and improve their overall well-being. Diets that focus on reducing saturated and trans fats, such as the Mediterranean diet or the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, have been shown to be effective in lowering cholesterol levels. These diets emphasize the consumption of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats like olive oil. Additionally, consuming foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, and lentils, can help decrease LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. Incorporating these dietary modifications can lead to significant improvements in cholesterol profiles and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
The Science Behind Fasting
 Source: www.frontiersin.org
Source: www.frontiersin.org
Fasting is a practice that has been used for centuries for various reasons, including spiritual, religious, and health purposes. From a scientific perspective, fasting has been shown to have several effects on the body, including its impact on cholesterol metabolism. During periods of fasting, the body enters a state of metabolic flexibility, where it switches from using glucose as its primary fuel source to utilizing stored fats. This shift in energy metabolism can lead to a decrease in levels of LDL cholesterol, commonly known as "bad" cholesterol, which is associated with an increased risk of heart disease. Additionally, research studies have found that fasting may also promote the production of HDL cholesterol, or "good" cholesterol, which helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. These mechanisms contribute to the beneficial effects of fasting on lowering cholesterol levels and potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases like high blood pressure and heart attacks.
How fasting affects cholesterol metabolism
 Source: fshn.illinois.edu
Source: fshn.illinois.edu
Fasting has been found to have a significant impact on cholesterol metabolism. When the body is in a fasting state, it starts to utilize stored fat for energy instead of relying on glucose from food. This process activates enzymes that break down cholesterol, resulting in a decrease in overall cholesterol levels. Additionally, fasting has been shown to increase the production of bile acids, which help remove excess cholesterol from the body. Studies have also shown that fasting can improve the balance between LDL (bad) and HDL (good) cholesterol, leading to improved cardiovascular health. Overall, fasting promotes a healthier cholesterol profile and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Research studies on the effects of fasting on cholesterol levels
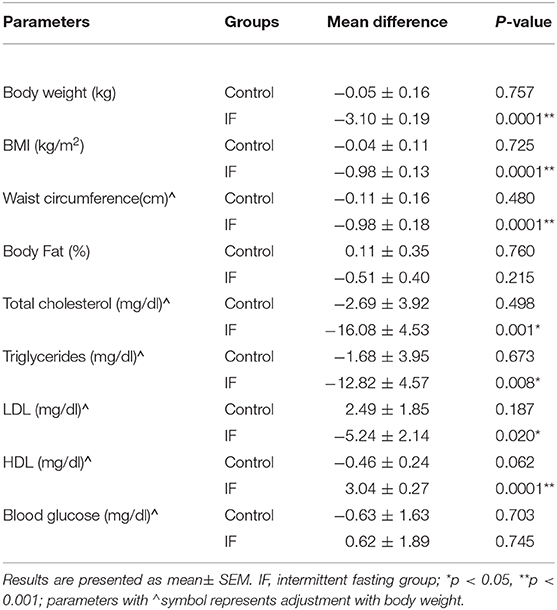 Source: www.frontiersin.org
Source: www.frontiersin.org
Numerous research studies have been conducted to examine the effects of fasting on cholesterol levels. One study published in the Journal of Nutritional Science found that intermittent fasting can significantly decrease total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides levels in individuals with obesity. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Lipidology demonstrated that fasting for 12 hours overnight can lead to a decrease in LDL cholesterol levels in individuals with dyslipidemia. Additionally, a review published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition reported that alternate-day fasting can result in improvements in blood pressure and cholesterol levels. These studies provide evidence supporting the role of fasting in lowering cholesterol.
The Science Behind Dieting
 Source: ideas.ted.com
Source: ideas.ted.com
Dieting is a scientifically proven method for lowering cholesterol levels. When individuals consume a healthy diet, their cholesterol intake is reduced and they also provide their body with essential nutrients. Numerous studies conducted by scientists have demonstrated the effectiveness of specific diets in reducing cholesterol. For example, the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like olive oil, has shown to have positive effects on cholesterol levels. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is another scientifically supported approach that not only helps lower blood pressure but also improves cholesterol profile. By understanding the science behind different diets and their impact on cholesterol metabolism, individuals can make informed decisions about their dietary choices to improve their overall health.
How specific diets influence cholesterol levels
 Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Specific diets can have a significant impact on cholesterol levels. For example, the Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil. This diet has been shown to lower LDL cholesterol (the "bad" cholesterol) levels and increase HDL cholesterol (the "good" cholesterol) levels, thus reducing the risk of heart disease. Similarly, the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats and sodium. This diet has been associated with lower blood pressure and improved cholesterol profiles. The American Heart Association also recommends the TLC (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) diet which includes reduced intake of saturated fats and dietary cholesterol for optimal cholesterol management.
Scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of dieting for cholesterol reduction
 Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Studies have shown that following a healthy diet can effectively lower cholesterol levels. The American Heart Association recommends a diet low in saturated fats and trans fats, while high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean sources of protein. One study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that participants who followed a low-fat diet experienced significant reductions in LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, a review of multiple studies published in the Archives of Internal Medicine confirmed that dietary interventions can lead to decreased LDL cholesterol levels and improved heart health. These findings provide strong scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of dieting for cholesterol reduction.
Fasting vs. Dieting: Pros and Cons
 Source: www.stylecraze.com
Source: www.stylecraze.com
When it comes to lowering cholesterol, both fasting and dieting have their pros and cons. Fasting, particularly intermittent fasting, can lead to weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity, which can have a positive impact on cholesterol levels. It also promotes autophagy, a process that helps clear out damaged cells and debris from the body. However, fasting may not be suitable for everyone and can lead to hunger and low energy levels.
On the other hand, dieting allows for a more sustainable approach to cholesterol management. Following a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or DASH diet recommended by the American Heart Association, can help reduce cholesterol levels. These diets emphasize whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods and saturated fats. However, sticking to a diet long-term can be challenging for some individuals.
Ultimately, the choice between fasting and dieting depends on individual preferences and medical considerations. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on any restrictive eating or fasting plans to ensure it aligns with one's specific health needs.
Advantages and disadvantages of fasting for lowering cholesterol
 Source: images.indianexpress.com
Source: images.indianexpress.com
One advantage of fasting for lowering cholesterol is the potential for weight loss. When we fast, our bodies start using stored fat as energy, which can lead to a decrease in body weight and therefore a reduction in cholesterol levels. Additionally, fasting has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood pressure, both of which are important factors in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
However, fasting may not be suitable for everyone. Some individuals may experience side effects such as headaches, fatigue, and irritability during extended periods of fasting. Additionally, it can be challenging to sustain a fasting routine long-term, making it less feasible as a permanent solution for managing cholesterol levels.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any fasting regimen to ensure it is appropriate for your individual health needs.
Advantages and disadvantages of dieting for cholesterol reduction
 Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Source: ars.els-cdn.com
When it comes to lowering cholesterol levels, dieting can be a highly effective approach. One of the major advantages of dieting is that it allows individuals to have more control over their food choices. By focusing on a heart-healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or DASH diet, individuals can consume foods that help lower bad cholesterol levels and promote overall cardiovascular health. Additionally, dieting often leads to weight loss, which in turn can contribute to reducing cholesterol levels. However, there are also some disadvantages to consider. Restrictive diets may be difficult to sustain long-term, leading to potential frustration and the temptation to revert back to unhealthy eating habits. Furthermore, certain dietary restrictions could potentially result in nutrient deficiencies if not properly planned and monitored. Therefore, it is important for individuals to work closely with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians when implementing a cholesterol-lowering diet to ensure nutritional needs are being met while effectively reducing cholesterol levels.
Which Method is More Effective?
When it comes to lowering cholesterol, both fasting and dieting have been shown to be effective methods. However, determining which method is more effective depends on various factors such as an individual's overall health, personal preferences, and lifestyle.
Fasting has been found to have positive effects on cholesterol levels. Intermittent fasting, for example, has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Some studies have also indicated that fasting can lead to weight loss, which can further contribute to improved cholesterol levels.
On the other hand, dieting can also play a significant role in lowering cholesterol. Following a heart-healthy diet, such as the one recommended by the American Heart Association, can help reduce LDL cholesterol. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins has been associated with lower cholesterol levels and improved heart health.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of either method will depend on an individual's commitment to their chosen approach and their ability to incorporate it into their daily routine. It may be beneficial for some individuals to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who specializes in cholesterol management to determine the best approach for their specific needs.
Comparison of the effectiveness of fasting and dieting in reducing cholesterol
 Source: fshn.illinois.edu
Source: fshn.illinois.edu
When it comes to reducing cholesterol levels, both fasting and dieting can be effective methods. Fasting has been shown to have a positive impact on cholesterol, particularly through intermittent fasting. This approach involves alternating periods of eating and fasting, which can lead to weight loss and improved cholesterol levels. On the other hand, dieting involves making conscious choices about what you eat, such as following a low-fat or low-cholesterol diet. By selecting heart-healthy foods and cutting back on saturated fats and cholesterol-rich foods, dieting can also help lower cholesterol levels. Ultimately, the effectiveness of each method may vary depending on individual factors such as overall health, adherence to the chosen approach, and genetic predisposition. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the most suitable method for reducing cholesterol levels effectively.
Factors to consider when choosing between fasting and dieting for cholesterol management
When determining whether to pursue fasting or dieting for cholesterol management, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, individuals should evaluate their personal preferences and lifestyle. Fasting requires periods of restricted eating or complete abstinence from food, while dieting involves making specific changes to one's eating habits. Additionally, one should take into account any existing medical conditions or dietary restrictions that may impact their ability to fast or adhere to certain diets. Lastly, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized guidance and recommendations tailored to an individual's unique health circumstances. Ultimately, the decision between fasting and dieting should be based on individual needs and capabilities for long-term cholesterol management.
Combining Fasting and Dieting
 Source: hips.hearstapps.com
Source: hips.hearstapps.com
Combining fasting and dieting can be a powerful approach for managing cholesterol levels. By integrating both methods, individuals can optimize their efforts to lower cholesterol and improve overall cardiovascular health. Fasting can help jumpstart the body's natural healing processes, while dieting ensures that cholesterol-lowering foods are being consumed regularly. By combining intermittent fasting with a heart-healthy diet recommended by organizations such as the American Heart Association, individuals can maximize the benefits of both approaches. This combination may lead to improved cholesterol levels, reduced blood pressure, and a decreased risk of heart disease. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on any fasting or dieting regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness.
The potential benefits of combining fasting and dieting for cholesterol control
Combining fasting and dieting can offer several potential benefits for cholesterol control. When these two methods are utilized together, they can work synergistically to optimize cholesterol-lowering effects.
Fasting helps to regulate cholesterol metabolism by reducing the production of LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing the breakdown of triglycerides. On the other hand, a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fat and high in fiber can further lower LDL cholesterol levels.
By incorporating both fasting and a cholesterol-lowering diet into a routine, individuals may experience enhanced cholesterol reduction. This combination approach may also lead to improvements in other cardiovascular risk factors such as blood pressure, as suggested by the American Heart Association.
However, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians before starting any fasting or dieting regimen to ensure its safety and effectiveness for individual needs.
Tips for incorporating both methods into a cholesterol-lowering routine
 Source: www.mayoclinic.org
Source: www.mayoclinic.org
When it comes to lowering cholesterol, combining fasting and dieting can be an effective approach. Here are some tips for incorporating both methods into a cholesterol-lowering routine:
- Consult with a healthcare professional: Before starting any fasting or dieting regimen, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide guidance tailored to your individual needs and medical history.
- Follow a balanced diet: Whether you're intermittent fasting or following a specific diet plan, make sure to focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Plan your meals: Meal planning is key in maintaining a healthy eating pattern during both fasting and non-fasting periods. This can help you stick to your cholesterol-lowering goals while ensuring adequate nutrition.
- Stay hydrated: It's important to stay hydrated throughout the day, especially during fasting periods. Drink plenty of water and consider incorporating herbal teas or infused water for added flavor.
- Monitor portion sizes: Even when following a specific diet plan or during fasting periods, portion control plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels. Be mindful of serving sizes and avoid overeating.
- Incorporate physical activity: Regular exercise is beneficial for overall heart health and can further support cholesterol reduction efforts. Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises such as brisk walking or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Seek support: Joining a support group or seeking the help of a registered dietitian can provide valuable guidance and encouragement throughout your cholesterol-lowering journey.
Remember that everyone's body is different, so finding the right balance between fasting and dieting may take some trial and error. Be patient with yourself and make adjustments as needed to achieve optimal results in improving your cholesterol levels.
Conclusion
 Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Source: ars.els-cdn.com
In conclusion, both fasting and dieting can be effective methods for lowering cholesterol levels. Fasting, particularly intermittent fasting, has shown promising results in reducing LDL cholesterol and improving overall cardiovascular health. On the other hand, certain diets, such as the Mediterranean diet and the DASH diet, have been scientifically proven to lower cholesterol levels. It is important to note that individual results may vary, and it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to one's diet or fasting routine. Additionally, combining fasting and dieting may provide even greater benefits for cholesterol control. Ultimately, the most effective approach for lowering cholesterol will depend on various factors including individual preferences, health conditions, and lifestyle considerations.
Summary of the key points discussed
Throughout this article, we delved into the topic of fasting vs. dieting in relation to their effectiveness in lowering cholesterol levels. We explored the definitions of cholesterol and its impact on health, as well as the different types of fasting and diets for reducing cholesterol. The science behind how fasting and dieting influence cholesterol metabolism was also examined, along with evidence from research studies supporting their effectiveness. We discussed the pros and cons of each method and compared their effectiveness. Additionally, we touched upon the potential benefits of combining fasting and dieting for better cholesterol control. Overall, this article aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of fasting and dieting as approaches to lower cholesterol levels.
Final thoughts on the most effective approach for lowering cholesterol
 Source: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Source: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
In conclusion, when it comes to lowering cholesterol levels, both fasting and dieting have their benefits and drawbacks. Fasting, particularly intermittent fasting, has shown promising results in reducing cholesterol levels and improving overall cardiovascular health. However, it may not be suitable for everyone and should be approached with caution, especially for those with certain medical conditions or nutrient deficiencies. On the other hand, following a cholesterol-lowering diet recommended by organizations like the American Heart Association can also effectively reduce cholesterol levels. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for individual needs. Combining both fasting and dieting may offer additional benefits for cholesterol management. Ultimately, the most effective approach will depend on individual preferences, goals, and health considerations.
