Fasting for Heart Health: Understanding the Link with Cholesterol
Introduction
 Source: www.heart.org
Source: www.heart.org
Maintaining good heart health is essential for overall well-being. High cholesterol levels are one of the major risk factors associated with poor cardiovascular health. There are various methods to manage and lower cholesterol levels, such as medication and dietary changes. However, fasting has emerged as a popular and effective way to reduce cholesterol numbers. Fasting not only helps in weight loss but also offers numerous benefits for heart health by controlling blood pressure, improving insulin sensitivity, and enhancing lipid metabolism. In this article, we will discuss how fasting can be beneficial in reducing bad LDL cholesterol, understanding what cholesterol is and its role in heart health, different types of fasting techniques such as intermittent fasting and extended fasting that aid in controlling elevated levels of cholesterol. Finally, we'll explore the importance of monitoring your cholesterol levels during fasts while highlighting the significance of regular medical consultations when dealing with high-cholesterol issues.
Understanding the importance of heart health and the link with cholesterol
 Source: images.everydayhealth.com
Source: images.everydayhealth.com
Reducing cholesterol levels is one of the primary methods to manage and improve heart health. Cholesterol is a fatty, wax-like substance found in all cells in our body. While it is essential for various bodily functions like hormone production and digestion, an excessive amount of cholesterol can lead to various health problems, especially cardiovascular diseases.
Cholesterol can cause plaque buildup inside arteries that restricts blood flow and increases the risk of heart attack or stroke. Bad LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is particularly responsible for this condition as it contributes to plaque formation whereas good HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol helps discard excess bad cholesterol from our bloodstream.
Hence, maintaining optimal cholesterol levels by reducing LDL levels while increasing HDL content remains an important aspect of ensuring good heart health. One effective method to achieve such results is through fasting which has gained significant popularity as a promising intervention strategy against high-cholesterol issues.
Why fasting can be beneficial for heart health
 Source: images.indianexpress.com
Source: images.indianexpress.com
Fasting has emerged as a popular technique to reduce cholesterol levels, which promotes heart health. When the body is in a fasting state, it uses stored glucose for energy and then turns towards fat reserves. This process results in weight loss and lowers triglycerides, both of which help lower bad LDL cholesterol levels.
Intermittent fasting is one type of fasting that may be beneficial for heart health. This involves short periods of caloric restriction or complete abstinence from food followed by periods of normal eating. Research indicates that intermittent fasting may improve blood pressure, blood sugar control, and cholesterol profiles.
Extended fasts lasting 24 hours or more also have potential benefits for heart health. These longer fasts enable the body to enter ketosis where it breaks down fat cells instead of glucose for fuel. When this occurs, the liver produces ketones that provide energy to the brain when glucose is scarce.
While more research is needed on extended fasts' long-term effects on heart health, it seems promising that using various types of fasting can benefit those seeking to improve their cardiovascular functions through maintaining consistent healthy cholesterol levels with occasional medical supervision.
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fatty substance that can be found throughout the body. While it is an essential component for cell membranes and hormone production, an excessive amount of cholesterol in the bloodstream can lead to various health problems, such as cardiovascular disease. Cholesterol is transported through the bloodstream by two types of lipoproteins: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL cholesterol is commonly referred to as "bad" cholesterol since it contributes to plaque buildup in arterial walls, while HDL cholesterol is known as "good" cholesterol because it carries excess LDL away from arteries. Maintaining healthy levels of both types of cholesterol can help prevent heart problems. It's important to understand what cholesterol is and how it affects overall heart health when exploring ways to lower its levels through fasting techniques such as intermittent fasting or extended fasting periods with medical supervision.
Explaining what cholesterol is and its role in heart health
 Source: healthmatters.nyp.org
Source: healthmatters.nyp.org
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that can be found in all cells of the body. It plays an important role in various bodily functions, such as cell membrane and hormone production. However, high levels of cholesterol can contribute to heart disease. In the bloodstream, cholesterol travels through two types of lipoproteins: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein). LDL is often referred to as "bad" cholesterol since it can accumulate on arterial walls and form plaques that narrow the blood vessels, leading to increased risk for heart attack or stroke. On the other hand, HDL acts like a scavenger by carrying excess LDL away from arteries and back to the liver for removal from the body. Understanding how cholesterol works in relation to heart health is crucial when considering ways to lower its levels and reduce risks associated with cardiovascular disease.
Differentiating between LDL cholesterol (bad) and HDL cholesterol (good)
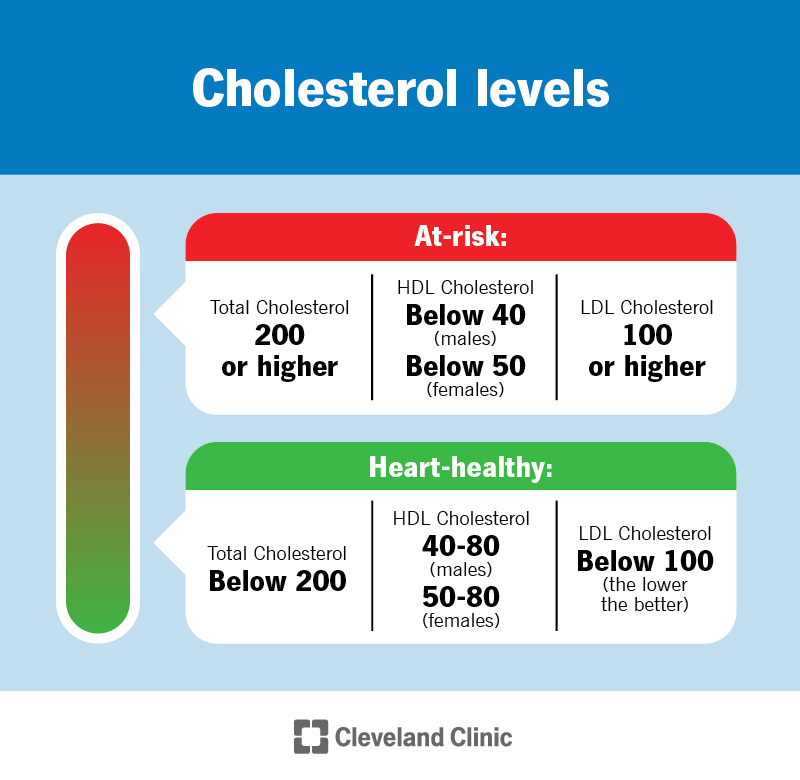 Source: my.clevelandclinic.org
Source: my.clevelandclinic.org
When considering the role of cholesterol in heart health, it is important to distinguish between low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, carries cholesterol from the liver to the body's tissues. However, too much LDL in the bloodstream can result in plaque formation on artery walls, which can lead to atherosclerosis and increased risk for heart disease. On the other hand, HDL acts like a scavenger by carrying excess cholesterol away from arteries and back to the liver for removal from the body. Consequently, high levels of HDL are associated with lower risks for cardiovascular disease. Maintaining optimal levels of both types of cholesterol plays an essential role in promoting overall heart health. By incorporating lifestyle changes such as fasting and exercise that positively affect lipid profiles in addition to consuming a healthy diet full of fruits and vegetables can help improve these key markers crucial for maintaining optimal cardivascular function .
The Benefits of Fasting for Heart Health
 Source: draxe.com
Source: draxe.com
Fasting has been shown to provide numerous benefits for heart health, including the reduction of cholesterol levels. When fasting, the body is forced to use stored fats as energy, which leads to a decrease in triglyceride levels and an increase in HDL cholesterol. Fasting also helps lower blood pressure, which is another important factor for heart health. High blood pressure puts increased stress on blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Intermittent fasting specifically has been shown to improve lipid profiles with reductions in total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol while maintaining or even increasing HDL (good) cholesterol. Extended fasting for several days may also help improve metabolic function by reducing insulin resistance.
However, it is important to note that while fasting can provide benefits for heart health, it should be approached with caution and under medical supervision particularly if an individual plans on doing extended fasts. It is crucial that individuals monitor their overall health during periods of fasting and consult their healthcare provider before beginning any new dietary routine
How fasting can help lower cholesterol levels
Fasting can provide benefits for heart health by helping to lower cholesterol levels. When the body enters a fasting state, it starts using stored fats as energy which results in a decrease in triglyceride levels and an increase in HDL cholesterol. This effect is particularly prominent during extended periods of fasting. Additionally, intermittent fasting has been shown to improve lipid profiles with reductions in total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol while maintaining or even increasing HDL (good) cholesterol. By reducing LDL levels that lead to plaque formation on the arteries, blood flow increases and risk of heart disease diminishes.
It is important to note that while fasting can offer benefits for lowering cholesterol levels, it should be viewed as part of an overall healthy lifestyle approach for improving heart health along with other changes such as exercise and balanced diet. Therefore, individuals who want to try this method should consult their healthcare provider before beginning any new dietary routine and monitor their overall health carefully during periods of fasting.
The impact of fasting on triglyceride levels
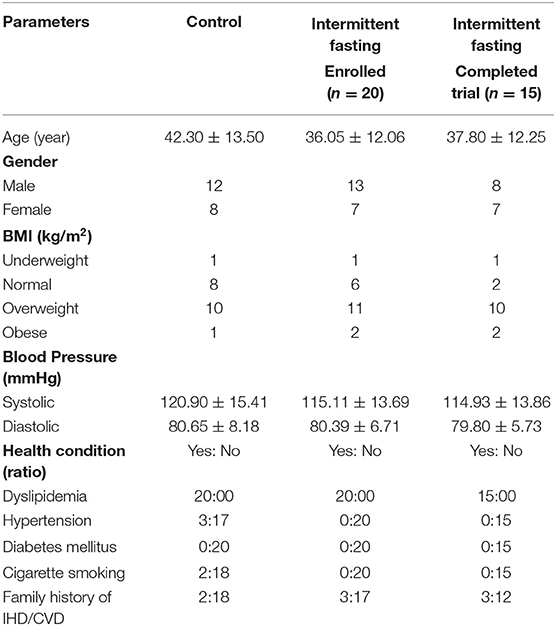 Source: www.frontiersin.org
Source: www.frontiersin.org
In addition to its cholesterol-reducing benefits, fasting has also been shown to have a positive impact on triglyceride levels. Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the bloodstream that can contribute to high blood pressure and increase the risk of heart disease. When someone fasts, their body begins using stored fats for energy, which results in lower levels of triglycerides in the bloodstream.
Extended periods of fasting have resulted in even greater reductions in triglyceride levels. Research studies have shown that extended periods of water-only fasting lasting up to 24 hours greatly reduce both total and non-fasting plasma triglycerides concentrations, making it effective for treating hypertriglyceridemia problems among other lipid metabolism disorders (LMD).
This effect may be particularly helpful for individuals with high triglyceride levels or other risk factors for heart disease such as obesity or diabetes. However, those interested in trying this method should consult their healthcare provider before embarking on an extended fast and build up gradually from smaller meals into bigger ones after they end their prolonged period fasts..
Types of Fasting
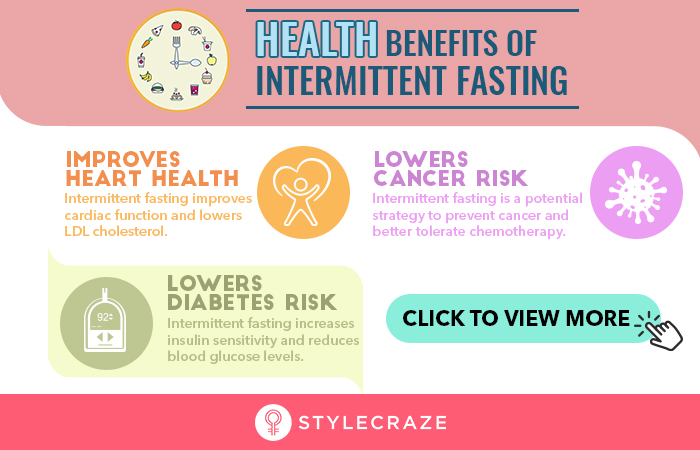 Source: cdn2.stylecraze.com
Source: cdn2.stylecraze.com
There are different types of fasting that one can try, each with its unique approach and benefits. One type is intermittent fasting, which involves alternating periods of eating and fasting. This approach has been found to help reduce bad LDL cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and aid in weight loss. Another type is extended fasting, which involves abstaining from food for more than 24 hours, up to several days or even weeks.
Extended fasts have shown potential benefits for heart health by reducing total cholesterol levels and triglyceride levels in the bloodstream. However, it's important to consult a healthcare provider before starting an extended fast as there may be risks involved if not done safely or properly.
Ultimately, choosing the right type of fasting should depend on one’s health goals and lifestyle needs. Whatever plan someone decides to follow should involve making sustainable changes that promote healthy living while being mindful of any pre-existing medical conditions or limitations they may have.
Intermittent fasting and its effects on cholesterol
 Source: www.startwellness.com
Source: www.startwellness.com
Intermittent fasting is a popular type of fasting that involves alternating periods of eating and fasting. Studies have shown that it can be particularly effective in reducing bad LDL cholesterol levels, which is important for heart health. During the periods of fasting, the body uses stored fat as energy, which leads to weight loss and an improvement in overall cholesterol levels.
Research has also discovered that intermittent fasting lowers blood pressure, another risk factor for heart disease. It works by activating certain genes responsible for improving lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. One study found an average reduction of 8% in total cholesterol levels among participants following this approach.
However, it’s worth noting that individuals should maintain a healthy diet during their eating periods instead of binging on unhealthy foods to reap maximum benefits from intermittent fasting practices. Nonetheless, intermittent fasting is a relatively simple plan with enormous potential rewards; those seeking to reduce their bad cholesterol levels may find this method helpful if done regularly and appropriately under medical supervision
Extended fasting and its potential benefits for heart health
 Source: www.stylecraze.com
Source: www.stylecraze.com
Extended fasting, also known as prolonged fasting, involves abstaining from food and calorie intake for an extended period of time, usually between 2-5 days. Recent studies suggest that this approach to fasting may have significant benefits for heart health. During times of prolonged fasting, the body enters a state called autophagy - a process where damaged cells are broken down and replaced with new ones.
Autophagy has been linked with improved cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation in the body and improving HDL cholesterol levels while decreasing triglycerides. Additionally, it can help reduce blood pressure and oxidative stress on the arteries which reduces the risk of developing heart disease.
Prolonged-fasting carries some risks if not monitored properly like dehydration or loss of muscle mass due to lack of protein but can be done safely under medical supervision.
Overall, extended-fasting has potential benefits for heart health by lowering bad LDL cholesterol levels and other risk factors associated with heart disease. However more research is required to study its long-term impacts on overall health before being considered as a routine practice for everyone.
Fasting and Weight Loss
 Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Source: ars.els-cdn.com
Incorporating fasting into a weight loss plan can have significant benefits for heart health. Fasting helps promote weight loss by reducing caloric intake, leading to a lower body mass index (BMI) and decreased risk of developing obesity-related diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
Intermittent fasting, in particular, has been shown to aid in weight loss while also improving cholesterol levels. Studies have found that intermittent fasting can reduce bad LDL cholesterol levels by up to 25%. It does this by reducing inflammation in the body and improving insulin sensitivity.
However, it is important to note that fasting should not be used as a sole method for long-term weight loss maintenance. A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial components for maintaining optimal heart health.
Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those who are underweight should consult with their healthcare provider before beginning any type of fast or dietary changes.
The connection between weight loss and improved heart health
 Source: keto-mojo.com
Source: keto-mojo.com
Weight loss can have a significant impact on heart health. When a person loses weight, they typically experience positive changes in their overall well-being and improved cardiovascular function. Excess body fat places additional strain on the heart by increasing blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
By losing weight, individuals can lower their risk of developing several obesity-related diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Studies have shown that even moderate weight loss (5-10% of total body weight) can lead to reduced LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, lowered blood pressure, and improved insulin sensitivity.
Fasting is one way to promote weight loss by reducing caloric intake; therefore incorporating it into a healthy lifestyle plan alongside regular exercise and balanced nutrition may offer additional benefits for optimal heart health. Consulting with a healthcare professional before beginning any form of dietary change or fast is always advisable for those who are overweight or obese.
How fasting can aid in weight loss and cholesterol reduction
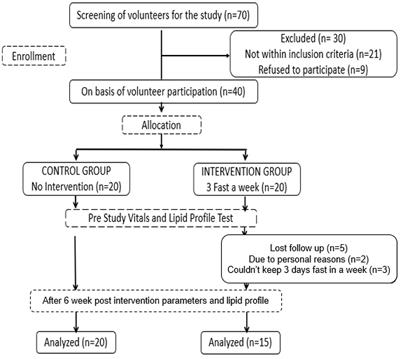 Source: www.frontiersin.org
Source: www.frontiersin.org
Fasting can aid in weight loss and cholesterol reduction by limiting calorie intake. When a person practices fasting, their body uses stored fat for energy instead of glucose from food. This results in weight loss and a decrease in the amount of circulating triglycerides - a type of fat that contributes to high levels of "bad" LDL cholesterol and low levels of "good" HDL cholesterol.
Furthermore, fasting may lead to decreased insulin resistance, which has been linked with metabolic syndrome and heart disease. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that intermittent fasting significantly reduces total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and blood pressure.
However, it is important to note that dietary habits during non-fasting periods play a crucial role in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels too. Consistent exercise combined with a balanced diet is necessary for sustainable weight loss and optimal heart health. Consultation with healthcare professionals before incorporating any dietary or lifestyle changes into one's routine is advisable for individuals who are overweight or have risk factors associated with heart disease.
Dietary Considerations during Fasting
 Source: www.jacc.org
Source: www.jacc.org
When practicing fasting for heart health, it is important to carefully consider dietary choices during both fasting and non-fasting periods. During a fast, individuals should focus on staying hydrated with water, herbal tea or black coffee and avoid consuming any calorie-containing foods.
During non-fasting periods, it is recommended that individuals make dietary decisions that will contribute towards healthy cholesterol levels. This can involve eating plenty of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables which can help regulate blood sugar levels. Consuming lean proteins like fish and chicken are also beneficial in maintaining optimal cholesterol levels while avoiding animal fats associated with high LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels.
It is crucial to avoid sugars, refined carbohydrates, and processed food items to maintain overall good health. Monitoring intake of saturated fats such as butter & palm oil can aid adequate control over lipid disorders leading to cardiovascular diseases.
Choosing nutrient-dense meals consistent with fresh whole grains along with regular exercise has significantly shown improvement in managing oxidative stress levels making your body less reactive towards harmful free radicals thereby increasing vascular protection.
Choosing heart-healthy foods during fasting periods
 Source: directorsblog.nih.gov
Source: directorsblog.nih.gov
During fasting periods, it is critical to choose heart-healthy foods that will not compromise cholesterol levels. Foods high in fiber like fruits and vegetables can assist with regulating blood sugar levels, while lean protein sources such as fish and chicken can help maintain optimal cholesterol balance without contributing saturated fats found in animal products linked to bad LDL cholesterol. It is important to avoid refined carbohydrates, processed food items, and sugars known for unfavorable health outcomes.
Individuals should consider incorporating plenty of nutrient-dense whole grains in their meals while also avoiding animal fats such as butter or palm oil; instead choosing plant-based alternatives such as olive oil which has been shown to have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. To further improve the benefits of fasting for lowering cholesterol levels, it is essential to observe regular exercise routines alongside healthy nutrition choices aimed at minimizing oxidative stress leading to vascular damage encouraging optimal long-term cardiovascular function.
The importance of balanced nutrition for optimal cholesterol levels
 Source: www.heart.org
Source: www.heart.org
During fasting periods, it is crucial to maintain a balanced and heart-healthy diet that will optimize cholesterol levels. A well-planned nutrition program must include various foods from different food groups for overall health and wellbeing. Optimal cholesterol balance is dependent on optimal nutritional intake.
Eating meals with whole foods and avoiding processed junk food can help limit the risks of elevated harmful LDL cholesterol that contributes to cardiovascular diseases. It’s essential to choose lean protein sources like fish and vegetable-based plant proteins instead of animal fats known for causing high levels of bad LDL cholesterol.
Furthermore, fiber-rich fruits, leafy greens, vegetables, nuts & seeds should be consumed during intermittent fasting as they promote elimination of toxins in the body that can lead to inflammation; which damages blood vessels leading to hypertension and hardening of arteries in the long run.
Plant-based alternatives such as olive oil are also perfect choices while observing fasting periods as research indicates their positive impact on cardiovascular health compared with regular dairy products loaded with saturated fats associated with compromised arterial functions. Maintaining a healthy environmental balance linked between nutritive intakes & physical activities is necessary for proper maintenance of optimal cardiovascular health status suited for one's age group & activity level throughout one's life cycle₁₂₃₄
Physical Activity and Fasting
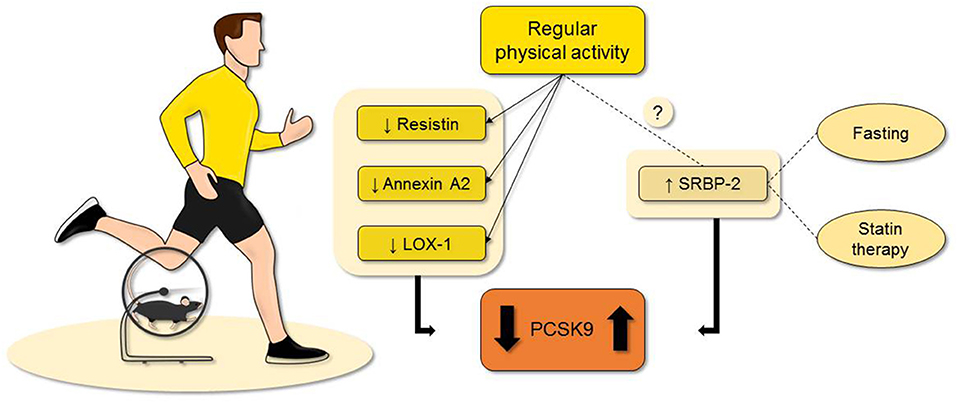 Source: www.frontiersin.org
Source: www.frontiersin.org
Physical activity is important for overall health, and it's no different during fasting periods. Exercise can help maintain muscle mass, aid in weight loss, and promote heart health by lowering blood pressure levels and improving circulation. When incorporating physical activity into a fasting regimen, it's necessary to listen to the body and engage in activities that don't lead to exhaustion or dehydration. Simple exercises like walking or yoga are great options for maintaining fitness levels while fasting. Additionally, scheduling exercise earlier in the day before breaking fast can help provide sustained energy throughout the day. However, those with pre-existing medical conditions should always consult with their doctor before engaging in any new physical activity routine.
By combining regular exercise with healthy dietary choices during intermittent fasting intervals, individuals may experience significant improvements in their heart health metrics such as lowered blood pressure and bad LDL cholesterol levels over time.
The role of exercise in promoting heart health
 Source: www.cardiacwellnessinstitute.com
Source: www.cardiacwellnessinstitute.com
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining optimal heart health. Physical exercise can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by lowering blood pressure levels, increasing circulation and improving cholesterol profiles. More specifically, engaging in regular aerobic or endurance exercise has been shown to lower bad LDL cholesterol levels while raising good HDL cholesterol levels. This ultimately leads to better heart health outcomes. In addition to these benefits, exercise can also help promote weight loss which further aids in reducing cholesterol and blood pressure readings.
It's important to note that incorporating physical activity into a fasting regimen should be done with caution, as it may lead to dehydration or exhaustion if not performed properly. Simple exercises like walking or yoga are great options for maintaining fitness during fasting periods. However, anyone with pre-existing medical conditions should consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on any new physical activity routine.
Tips for incorporating physical activity during fasting
 Source: www.frontiersin.org
Source: www.frontiersin.org
During fasting, it's important to maintain an active lifestyle for optimal heart health. However, exercise during periods of low food intake can be challenging. To incorporate physical activity during fasting, individuals should start with lighter activities such as walking or stretching. This will help prevent exhaustion and dehydration due to lack of energy. It's essential to listen to the body and rest as needed since overexertion can lead to negative consequences for heart health.
Additionally, workouts should be timed appropriately so they don't interfere with meals or sleep patterns. High-intensity exercises may not be suitable during a fast but could instead be done during a non-fasting period when energy levels are higher.
If uncertain about how much exercise is appropriate during a fast, speaking with a doctor or trainer who specializes in intermittent fasting could provide valuable insight on starting an exercise regimen that works best for individual circumstances.
Monitoring Cholesterol Levels during Fasting
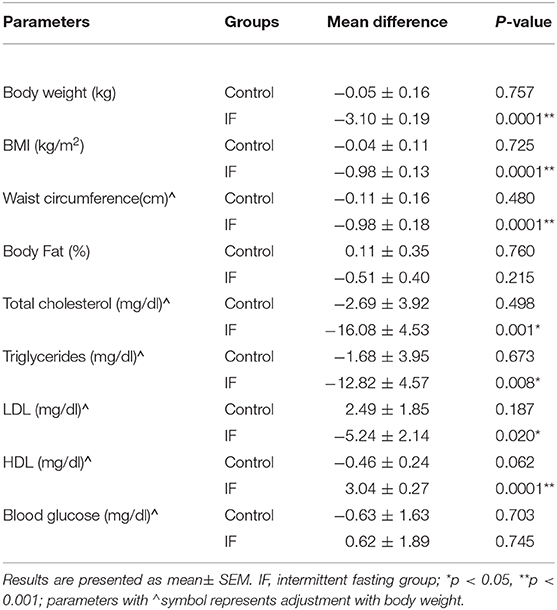 Source: www.frontiersin.org
Source: www.frontiersin.org
It is important to monitor cholesterol levels while fasting to ensure that the body is responding positively and to identify any potential issues. Regular check-ups with a doctor or healthcare provider can provide valuable insight into an individual's cholesterol levels and their overall heart health.
There are several ways to track cholesterol levels during fasting, such as blood tests before, during, and after the fast. A lipid panel test can measure LDL (bad) cholesterol as well as HDL (good) cholesterol and triglycerides.
In addition to monitoring cholesterol levels, it is also essential to keep tabs on other factors that impact heart health such as blood pressure.
Checking up regularly with a medical professional can help individuals make informed decisions about their fasting regimen by potentially adjusting dietary habits or adding in more physical activity based on test results. Working together with a medical team can optimize one’s chances of experiencing positive changes in their health through fasting.
How to track cholesterol levels while fasting
There are several ways to monitor cholesterol levels while fasting. One common method is through regular blood tests, including lipid panel tests which examine LDL (bad) and HDL (good) cholesterol, as well as triglycerides. These tests can be administered prior to beginning a fast, during the fast itself, and after the fast has been completed.
Another way to track cholesterol levels during fasting may involve maintaining a food journal or log of meals consumed in order to identify any foods that may contribute towards high cholesterol levels. Additionally, individuals may consider investing in home testing kits that measure their total cholesterol levels and other important biomarkers related to heart health such as blood pressure. Keeping tabs on these markers throughout different stages of fasting can provide valuable insight into an individual's overall cardiovascular health and whether there are changes that need to be made for optimal outcomes.
The importance of regular check-ups and medical advice
 Source: www.heart.org
Source: www.heart.org
While fasting can have significant health benefits, it is important to monitor cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health regularly. Medical check-ups are a crucial component of staying on top of heart health, and individuals should consult with their healthcare providers before starting any fast or changing their diet.
Doctors can perform blood tests that help measure cholesterol levels and identify any other risk factors for heart disease, like high blood pressure. They may also offer advice about what kinds of foods to eat during periods of fasting in order to provide the body with the necessary nutrients while still promoting weight loss and improved cholesterol levels.
Regular medical check-ups can help individuals track their progress over time and make any necessary adjustments to ensure they stay on the right path towards optimal heart health. In addition, anyone experiencing symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath while fasting should seek medical attention immediately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fasting can provide numerous benefits for heart health by helping to lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Intermittent fasting has been shown to be particularly effective in reducing bad LDL cholesterol while increasing good HDL cholesterol. Extended fasting may also have potential benefits, but it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any prolonged fasts.
Fasting can also aid in weight loss, which further improves cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. It is essential to choose heart-healthy foods during periods of fasting as proper nutrition remains critical for optimal cholesterol levels.
Physical activity should also be encouraged during periods of fasting as exercise plays a crucial role in promoting heart health along with dietary modifications.
Regular medical check-ups are necessary while making significant changes in diet or beginning new therapeutic interventions such as fasting. By following these guidelines and monitoring their progress, individuals can achieve improved heart health and overall wellness over time.
Summary of the benefits of fasting for heart health
 Source: whatsgood.vitaminshoppe.com
Source: whatsgood.vitaminshoppe.com
Fasting has been shown to provide numerous benefits for heart health by helping to lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Intermittent fasting, in particular, has been found to be effective in reducing bad LDL cholesterol while increasing good HDL cholesterol. Extended periods of fasting may also have potential cardiovascular benefits, such as reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Moreover, fasting can aid in weight loss, which further improves cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. However, it is essential to choose healthy foods during periods of fasting as proper nutrition remains critical for optimal cholesterol levels.
Physical activity should also be encouraged during fasts as exercise plays a significant role in promoting heart health along with dietary modifications. Regular check-ups and medical advice are necessary when making changes related to diet or beginning new therapeutic interventions such as fasting.
Overall, incorporating intermittent or extended fasting into one's lifestyle could lead to improved heart health and wellness over time.
Key takeaways and future considerations
 Source: www.cardiacwellnessinstitute.com
Source: www.cardiacwellnessinstitute.com
Fasting has been shown to offer many benefits for improving heart health by lowering cholesterol levels and reducing blood pressure. Intermittent fasting, in particular, can help lower bad LDL cholesterol and increase good HDL cholesterol, while extended periods of fasting may also reduce inflammation and oxidative stress that are associated with heart disease.
Furthermore, when combined with proper nutrition and exercise, fasting can aid in weight loss that further contributes to improving overall cardiovascular health. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before beginning any new dietary or lifestyle changes such as fasting.
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels during the fast is important to evaluate its effectiveness in promoting heart health while minimizing potential risks. These key takeaways underscore the importance of working with a healthcare professional alongside incorporating an intermittent or extended period of fasting into daily wellness practices for those concerned about their heart health. Future research endeavors are needed to further our understanding of the effects of other types or durations of fasting on different factors influencing heart health such as triglycerides and inflammation markers.
