Exploring the Science Behind Heart Disease Prevention: What Helps Reduce the Risk?
Understanding Heart Disease Prevention
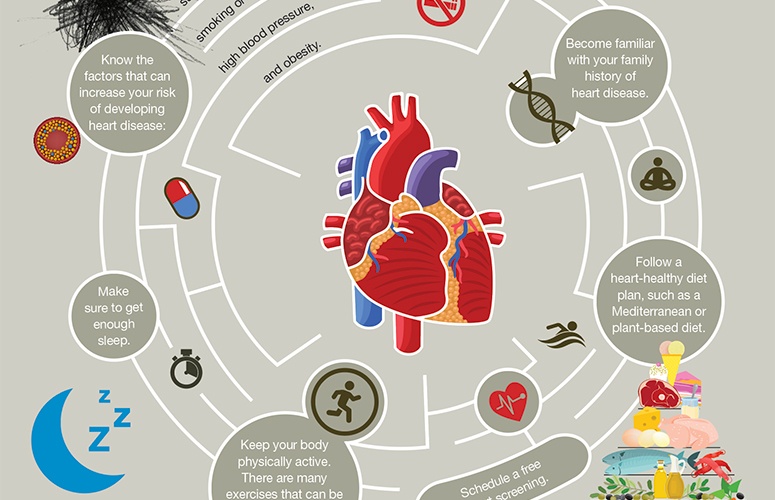
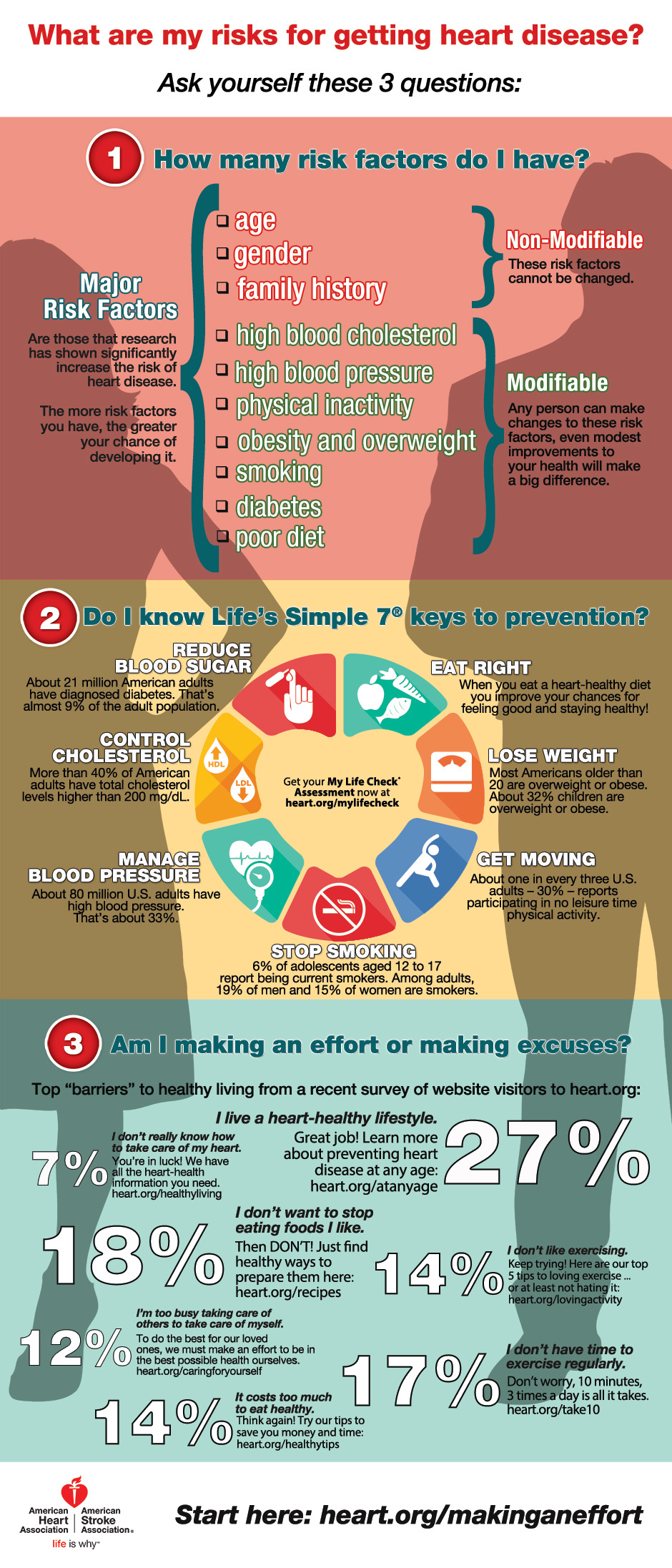
What is heart disease and its risk factors
Heart disease refers to a range of conditions that affect the heart's structure and function, often leading to serious health complications. The most common type of heart disease is coronary artery disease, which occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. Other types of heart disease include heart failure, arrhythmias, and heart valve problems.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of heart disease. Some of the primary factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes, and a family history of heart disease. These risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing heart disease and should be closely monitored and managed to reduce the risk.
Lifestyle changes for heart disease prevention
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart disease. Here are some key changes individuals can make to improve their heart health:
- Adopt a Healthy Diet: Consuming a diet low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium, while rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help lower the risk of heart disease. Incorporate foods like salmon, avocados, nuts, and olive oil into your diet.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Incorporate activities like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing into your routine.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels, increases blood pressure, and promotes the development of fatty deposits on artery walls, increasing the risk of heart disease. Quitting smoking is one of the most significant steps an individual can take for their heart health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to the development of heart disease. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, practicing mindfulness, or engaging in hobbies can help manage stress levels and promote heart health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for heart disease. By maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, individuals can lower their risk of developing heart-related conditions.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, individuals can lower their risk of heart disease and improve their overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding heart disease prevention is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. By identifying the risk factors associated with heart disease and adopting lifestyle changes that promote cardiovascular health, individuals can reduce their risk of developing heart-related conditions. Remember, prevention is key, and small changes in daily habits can lead to significant improvements in heart health.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet for Heart Health
The role of nutrition in heart disease prevention
Maintaining a healthy diet is integral to heart disease prevention. Nutrition plays a vital role in reducing the risk of heart disease and promoting overall cardiovascular health. A diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium, while being rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can significantly lower the risk of developing heart-related conditions.
Key dietary recommendations for reducing heart disease risk
- Limit saturated and trans fats: Diets high in saturated and trans fats can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Opt for healthier fats such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and oily fish like salmon.
- Reduce sodium intake: High sodium intake can contribute to high blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease. Limit the consumption of processed and packaged foods, as they often contain high levels of sodium. Instead, season your meals with herbs and spices to add flavor without the extra sodium.
- Incorporate fiber-rich foods: Consuming a diet rich in fiber has been shown to lower the risk of heart disease. Include foods like whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables in your meals to increase your fiber intake.
- Choose lean proteins: Protein is an essential part of a healthy diet, but not all sources are heart-healthy. Opt for lean proteins such as skinless poultry, fish, beans, and legumes. Limit the consumption of red meat and processed meats, which have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
- Include heart-healthy fats: Not all fats are bad for you. Consuming healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, can have a positive impact on heart health. These fats can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Watch portion sizes: Even healthy foods should be consumed in moderation. Pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating, as excess calories can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of heart disease.
By following these key dietary recommendations, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall cardiovascular health. Making these changes can be challenging at first, but with time and perseverance, they can become lifelong habits that contribute to a healthier heart. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to receive personalized advice and guidance on adopting a heart-healthy diet
The Importance of Regular Exercise
How physical activity helps lower the risk of heart disease
Regular exercise and physical activity play a crucial role in reducing the risk of heart disease. Physical activity helps strengthen the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health. When you engage in regular exercise, several positive changes occur within your body that contribute to a healthy heart.
Firstly, exercise helps to lower blood pressure. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease, and by staying active, you can help keep your blood pressure in a healthy range. Exercise also helps to reduce LDL cholesterol levels, commonly known as 'bad' cholesterol, and increase HDL cholesterol levels, also known as 'good' cholesterol. This is important because high levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Regular physical activity is also effective in managing weight. Obesity and excess body weight are linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Exercise helps control weight by burning calories and building lean muscle mass. Additionally, physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, which is closely associated with heart disease.
Exercise has other positive effects on heart health as well. It improves blood circulation, allowing oxygen and nutrients to be delivered more efficiently to the heart and the rest of the body. It also improves the function of the blood vessels, making them more flexible and capable of dilating and constricting as necessary.
Different types of exercises for heart health
To reap the benefits of exercise for heart health, it is important to engage in a combination of aerobic exercises and strength training.
Aerobic exercises, also known as cardio exercises, raise your heart rate and increase your breathing. Examples include brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, and dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
Strength training exercises should also be incorporated into your routine. These exercises work your muscles and help maintain bone density. Examples include lifting weights, using resistance bands, and doing bodyweight exercises. Aim for strength training exercises at least two days a week, targeting all major muscle groups.
In addition to aerobic and strength training exercises, incorporating flexibility exercises such as stretching and yoga can help improve overall mobility and prevent injuries.
It is important to note that before starting any exercise program, especially if you have underlying health conditions, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized recommendations and guidance based on your specific needs.
By making regular physical activity a part of your lifestyle, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve your overall cardiovascular health. Remember, consistency is key, and even small increments of exercise can make a big difference in protecting your heart.
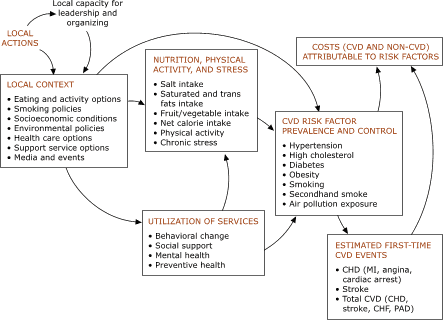
 Source: livewellsiouxfalls.org
Source: livewellsiouxfalls.org
Stress Management and Heart Disease
The connection between stress and heart disease
When it comes to the prevention of heart disease, managing stress plays a crucial role. The connection between stress and heart disease has been extensively studied, and research has shown that chronic stress can significantly increase the risk of developing cardiovascular issues. This is because stress activates the body's "fight or flight" response, leading to an increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and the release of stress hormones like cortisol. Over time, this chronic activation of the stress response can contribute to the development of heart disease.
Effective stress reduction techniques for heart health
To reduce the risk of heart disease, it is essential to incorporate effective stress reduction techniques into your daily routine. Here are some strategies that have been found to be beneficial:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity not only improves cardiovascular health but also helps reduce stress levels. Engaging in activities like walking, jogging, or yoga can help relax the mind and release endorphins, the body's natural mood boosters.
- Relaxation techniques: Practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the mind and reduce stress. These techniques can be easily incorporated into your daily routine and provide immediate relief from stress and anxiety.
- Social support: Connecting with loved ones, friends, and support groups can help alleviate stress. Having a strong support system to share your concerns and experiences with can provide emotional support and promote a sense of belonging, reducing stress levels.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Eating a well-balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol and tobacco use are essential for overall heart health. These healthy lifestyle choices contribute to stress reduction and decrease the risk of heart disease.
- Time management: Effective time management techniques, such as setting priorities, delegating tasks, and practicing self-care, can help reduce stress levels. By organizing your time and maintaining a healthy work-life balance, you can minimize the impact of stress on your overall well-being.
- Seeking professional help: If stress and anxiety persist or become overwhelming, it's important to seek help from a mental health professional. They can provide guidance and support to develop personalized stress management strategies and help address any underlying issues contributing to stress.
Incorporating these stress reduction techniques into your daily life can help lower the risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health. By managing stress effectively, you can promote a healthier lifestyle and increase your chances of maintaining a strong heart for years to come. Remember, taking care of your mental well-being is just as important as taking care of your physical health.
Other Factors in Heart Disease Prevention
The impact of smoking on heart health
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for heart disease and its detrimental effects on cardiovascular health cannot be overstated. When you smoke, the chemicals present in tobacco can damage your blood vessels, causing them to narrow and harden. This, in turn, increases blood pressure and reduces blood flow to the heart, raising the risk of heart disease.
Cigarette smoke also contains high levels of carbon monoxide, which replaces oxygen in the blood, leading to an increased workload on the heart. Additionally, smoking raises the levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) while lowering the levels of good cholesterol (HDL), further contributing to the risk of heart disease.
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to reduce your risk of heart disease. Within just a few years of quitting, your risk decreases significantly, and over time, it becomes comparable to that of a nonsmoker. Seeking support from healthcare professionals and utilizing smoking cessation methods, such as nicotine replacement therapy or medications, can greatly increase the chances of successfully quitting smoking.
The role of sleep and managing chronic conditions
Getting adequate sleep is crucial for overall health, including heart health. Research has shown that poor sleep quality and duration increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Lack of sleep can disrupt the body's hormonal balance, leading to higher levels of stress hormones and inflammation, which are known risk factors for heart disease.
Chronic conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, also play a significant role in heart disease prevention. These conditions put added strain on the cardiovascular system, making individuals more susceptible to heart disease. Managing these conditions through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups with healthcare professionals is essential in reducing the risk of heart disease.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, is crucial in preventing heart disease. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while avoiding processed foods and excessive salt and sugar intake, can help support heart health. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and strength training, helps improve cardiovascular fitness, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
In conclusion, in addition to managing stress, other factors play a significant role in heart disease prevention. Quitting smoking, getting enough sleep, and effectively managing chronic conditions can greatly reduce the risk of heart disease. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, seeking healthcare support, and making necessary changes, individuals can take control of their heart health and significantly improve their overall well-being. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to maintaining a strong and healthy heart.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heart disease prevention is a multifaceted approach that involves addressing various factors that contribute to its development. By understanding the impact of smoking on heart health and the role of sleep and managing chronic conditions, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing their risk. Additionally, combining strategies and adopting a healthy lifestyle can further optimize heart disease prevention efforts.
Combining strategies for optimal heart disease prevention
When it comes to heart disease prevention, it is important to combine various strategies for optimal results. Quitting smoking, one of the most significant risk factors, should be prioritized. Seeking support from healthcare professionals and utilizing smoking cessation methods can greatly increase the chances of successfully quitting smoking.
In addition to quitting smoking, getting adequate sleep plays a crucial role in heart health. Prioritizing sleep and implementing healthy sleep habits can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a peaceful sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bed.
Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol is also crucial in reducing the risk of heart disease. This involves regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, taking prescribed medications, and making necessary lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity.
Taking proactive steps for a healthier heart
Taking proactive steps towards a healthier heart involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes following a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while avoiding processed foods and excessive salt and sugar intake. Regular exercise, including aerobic exercises and strength training, helps improve cardiovascular fitness, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Additionally, managing stress plays a significant role in heart disease prevention. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy and relaxation can help reduce the impact of stress on heart health.
When it comes to heart disease prevention, individuals have the opportunity to take control of their health and significantly improve their overall well-being. By combining strategies, seeking healthcare support, and making necessary lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease and maintain a strong and healthy heart for years to come. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to heart health, and the proactive steps taken today can have a significant impact on long-term well-being.