Does kombucha help with gut inflammation?
If you've been keeping an eye on the ever-evolving world of health and wellness trends, there's no doubt that you've come across kombucha at some point. This fizzy, fermented tea has taken grocery store shelves by storm and is increasingly being hailed as a go-to remedy for various ailments. With its long history, known for improving digestion and boosting the immune system, it's hard not to wonder: Does kombucha really help with gut inflammation? In this post, we'll take a deep dive into the world of kombucha and explore the science behind this trendy beverage to help you decide whether this magical elixir lives up to its gut healing claims. Buckle up, and let's embark on an effervescent journey together!
 Source: pub.mdpi-res.com
Source: pub.mdpi-res.com
Introduction to Kombucha: An Overview
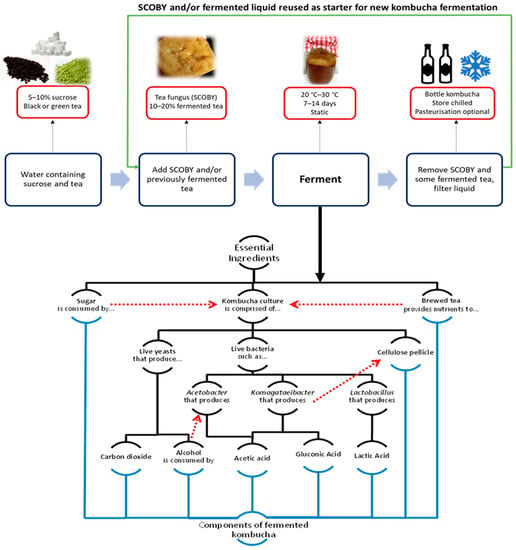
Kombucha is an ancient fermented beverage that has gained popularity in recent years, primarily due to its purported health benefits. Dating back over 2000 years, this fizzy drink is made from tea, sugar, and a specific culture of bacteria and yeast, which gives it its distinctive tangy taste and slightly alcoholic content. After fermenting for a week to a month, the final product is a light, carbonated beverage that appeals to those looking for a healthier alternative to soda or other sugar-laden drinks.
One of the key reasons behind kombucha's surge in popularity is its rich source of probiotics and beneficial compounds, such as antioxidants and polyphenols. These compounds have been linked to numerous health benefits, including improved digestion, weight management, and reduced inflammation. Consequently, kombucha is often promoted as a functional beverage that can assist in maintaining and promoting a healthy gut, among other potential health benefits. However, it is important to note that scientific research on kombucha remains limited, and more studies are required to fully understand its true impact on gut health and inflammation. [1][2]
 Source : www.wfla.com
Source : www.wfla.com
The Fermentation Process and Probiotic Benefits
The fermentation process of kombucha is quite fascinating, as it involves the addition of specific strains of bacteria, yeast, and sugar to black or green tea, which is then allowed to ferment for a week or more. During this period, bacteria and yeast form a mushroom-like film on the surface of the liquid, giving kombucha its nickname, "mushroom tea".
This blob, called a SCOBY (Symbiotic Colony of Bacteria and Yeast), can be used to ferment new batches of kombucha. The result is a slightly carbonated beverage that is rich in acetic acid, other acidic compounds, and trace amounts of alcohol.
Kombucha's fermentation process is believed to provide various health benefits, particularly due to its probiotic properties. Although there is still limited evidence to support the probiotic benefits of kombucha, it is known to contain several species of lactic acid bacteria, which may help improve gut health. Probiotics are essential for supplying the gut with healthy bacteria, which in turn can improve digestion, reduce inflammation, and boost the immune system. As such, incorporating kombucha into one's diet may be beneficial for individuals experiencing gut inflammation or other digestive issues. [3][4]
 Source: marcellepick.com
Source: marcellepick.com
Limited Research on Kombucha Health Claims
Although kombucha has gained immense popularity in recent years, research on its health claims remains limited. The fermented tea beverage contains probiotics, which are healthy microbes that may provide various benefits for the body. Some of these benefits are similar to those of other fermented foods such as sauerkraut, pickles, kimchi, kefir, and yogurt. However, quality studies supporting kombucha's potential role in improving health are sparse.
While some compounds found in kombucha have been associated with positive effects on the body, it is important to remain cautious about solely relying on kombucha for improved health. Expert dietitians suggest that kombucha may be a useful addition to an overall healthy diet and lifestyle, but it should not be mistaken as a magic elixir for all health ailments. [5][6]
 Source: www.reead.com
Source: www.reead.com
Examining Claims of Kombucha and Weight Loss
Kombucha, a fermented tea beverage, has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its potential health benefits. One such claim is that it can aid in weight loss. While it may not be a magic potion to help shed those extra pounds, incorporating kombucha into a balanced diet and exercise routine could have some benefits.
Firstly, kombucha is known to be a good source of probiotics, which may play a role in supporting a healthy digestive system. A healthy gut can, in turn, contribute to better weight management. Additionally, kombucha made from green tea boasts polyphenols and may even have some of the same benefits as green tea, such as boosting metabolism and promoting fat burning.
However, it is essential to choose the right kombucha to enjoy these benefits. Opt for varieties with lower sugar content and be mindful of serving sizes. Ultimately, kombucha can be a beneficial addition to a healthy lifestyle, but weight loss will require a more comprehensive approach of a balanced diet and consistent exercise. [7][8]
 Source: www.netmeds.com
Source: www.netmeds.com
Kombucha and Gut Health
Kombucha, a fermented tea drink, is believed to have numerous health benefits, including supporting gut health. While there is not enough scientific evidence to draw definitive conclusions about the drink's impact on gut inflammation, kombucha is rich in probiotics due to its fermentation process. Probiotics provide the gut with healthy bacteria, aiding digestion and balancing the microbiome.
Some nutrition experts believe that the probiotics in kombucha may contribute to improved gut health by reducing inflammation and providing antioxidants. However, it is important to note that more research is needed in order to confirm these claims. Registered dietitian Maria Zamarripa emphasizes that kombucha should not be used as a substitute for a healthy diet rich in fiber, which promotes a healthy gut environment for probiotics to thrive. [9][10]
 Source: wumountaintea.com
Source: wumountaintea.com
Systematic Review of Kombucha's Effects on the Gut Microbiota
Kombucha, a fermented nonalcoholic tea-based beverage, has gained widespread popularity for its potential health benefits. Through a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeasts, studies have shown its antimicrobial, antioxidant, antiproliferative, and anti-carcinogenic properties. Recently, a systematic review has been conducted to evaluate the effects of kombucha consumption on the gut microbiota and obesity-related comorbidities.
The review's findings indicate that kombucha consumption may help attenuate oxidative stress and inflammation, improve liver detoxification processes, and reduce intestinal dysbiosis. This beneficial impact could be valuable for controlling and treating obesity, as well as its associated comorbidities. Furthermore, kombucha has also been shown to positively modulate the gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in maintaining intestinal health. However, more research involving human subjects is required to corroborate these findings and further explore kombucha's potential in promoting gut health and reducing inflammation. [11][12]
 Source: post.greatist.com
Source: post.greatist.com
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties of Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea drink that has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential health benefits. One of these benefits is its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This fermented beverage is made from either green or black tea and contains a range of healthy bacteria, yeasts, and organic acids which can improve gut health, digestion, and inflammation.
The antioxidant properties of kombucha are attributed to the polyphenols found in tea. These polyphenols can help neutralize harmful free radicals, which are reactive molecules that can cause cellular damage and contribute to inflammation. Additionally, kombucha contains acetic acid and other organic acids that can have anti-inflammatory effects.
Some studies have shown that certain compounds in kombucha, such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), can protect cells from damage and reduce inflammation. This may be beneficial for individuals suffering from inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. However, more research is needed to confirm the effectiveness of kombucha for gut inflammation specifically.
Overall, incorporating kombucha into your diet can be a delicious way to increase your intake of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds, which may help improve gut health and reduce inflammation. [13][14]
 Source: draxe.com
Source: draxe.com
Kombucha's Ability to Improve Liver Detoxification Processes
Kombucha, a fermented tea-based beverage, has long been praised for its numerous health benefits. One of its most notable properties lies in its ability to support and improve liver detoxification processes. The liver is a vital organ responsible for filtering out toxins and harmful substances from the body. By assisting the liver in this crucial task, kombucha can help maintain overall health and well-being.
This liver-supporting effect can be attributed to the powerful antioxidants present in kombucha, which combat free radicals and prevent cellular damage. Furthermore, the fermentation process involved in kombucha production generates lactic acid bacteria, which have probiotic functions and can enhance gut health. Since a healthy gut is closely linked to liver function, consuming kombucha can contribute to maintaining a well-functioning liver and preventing various chronic disorders. Thus, incorporating kombucha into one's daily routine can be a simple yet effective way to support liver detoxification and promote optimal health. [15][16]
 Source: i0.wp.com
Source: i0.wp.com
Reduction of Intestinal Dysbiosis through Kombucha Consumption
Kombucha, a fermented tea rich in probiotics and beneficial compounds, has been gaining attention for its potential to improve gut health and reduce inflammation. One of the main benefits of kombucha consumption is the reduction of intestinal dysbiosis, a condition wherein the balance of good and bad bacteria in the gut is disrupted. This imbalance can lead to a variety of gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, nausea, and inflammation.
Incorporating kombucha into one's daily diet is believed to help restore the balance in gut bacteria, thanks to its probiotic content that promote the growth of good bacteria. Studies have shown that kombucha, especially when made from green and black tea, has the ability to modulate the gut microbiota, improving overall digestion and intestinal health. Consequently, a healthy gut can lead to a reduced risk of other health issues, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even certain types of cancer.
In summary, regular consumption of kombucha can help to alleviate intestinal dysbiosis, thereby promoting a healthy gut environment and reducing inflammation. This refreshing and fizzy drink, containing a blend of nutritious ingredients, offers a delicious and easy way to improve gut health and overall well-being. [17][18]
 Source : ars.els-cdn.com
Source : ars.els-cdn.com
Kombucha's Potential as a Treatment for Obesity and Associated Comorbidities
Kombucha, a fermented tea-based beverage, has garnered attention for its potential health benefits, particularly in relation to obesity and its associated comorbidities. Studies suggest that consuming kombucha may help attenuate oxidative stress and inflammation, improve liver detoxification, and reduce intestinal dysbiosis. These properties make it a promising option for the management and treatment of obesity and related issues.
The presence of beneficial compounds such as phenolic compounds in kombucha is believed to contribute to its positive effects on gut health. Moreover, the drink's probiotic content may help balance the intestinal flora and alleviate inflammation. Furthermore, kombucha made with green tea contains a compound called epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) which has the potential to boost metabolic rates in adults, aiding in weight management.
Despite these promising findings, it is important to note that research on kombucha is still limited, and further studies are needed to solidify the potential benefits of its consumption. Nonetheless, incorporating kombucha into one's diet could complement a healthy lifestyle and potentially improve gut health and inflammation. [19][20]
